7 CI/CD for Machine Learning
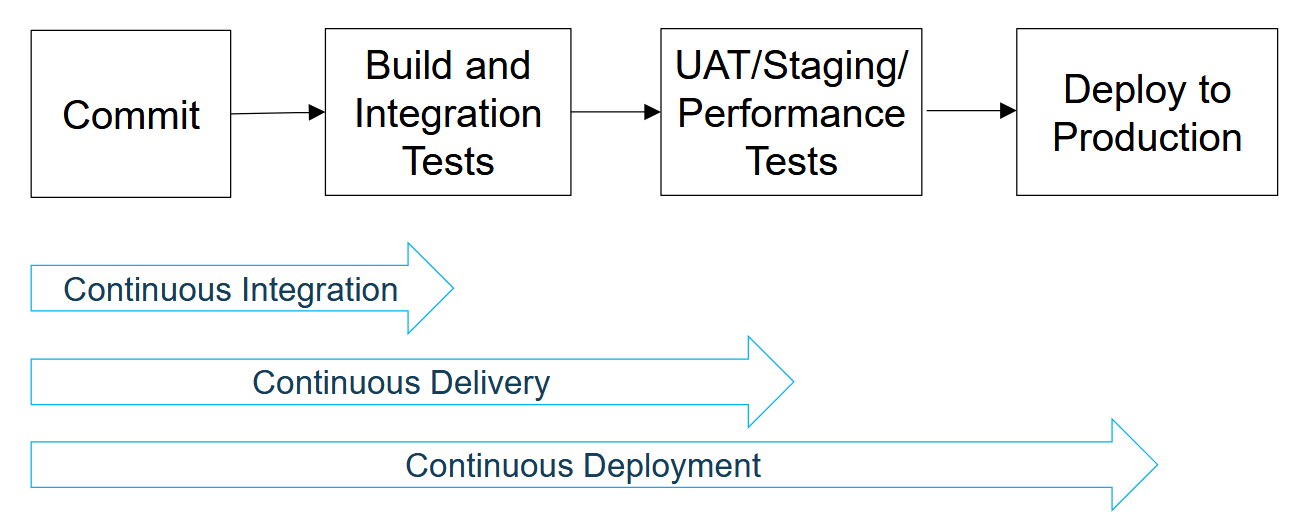
- Commit: Developers commit changes to the version control system.
- Build and Integration Tests: Automated build processes and integration tests are executed to ensure code consistency.
- UAT/Staging/Performance Tests: User Acceptance Testing (UAT), Staging, and Performance tests are performed to validate functionality and performance.
- Deploy to Production: The application is deployed to the production
- Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of automating the integration of code changes from multiple contributors into a single software project. The main goals are to detect integration issues early, improve code quality, and reduce the time it takes to deliver new features.
- Continuous Delivery (CD) is the practice of automating the deployment of code changes to production or staging environments. The main goals are to ensure that software can be released reliably and frequently, and to reduce the time it takes to deliver new features to users.
- Continuous Deployment is an extension of Continuous Delivery where every change that passes automated tests is automatically deployed to production without manual intervention.
7.1 DevOps and MLOps
DevOps is a set of practices that emphasize automation and collaboration between development and operations teams with the purpose of reducing time to deploy new features.
MLOps is a set of practices that emphasize automation and collaboration between development, operations teams, and data scientists with the purpose of reducing time to deploy new features and models.